

Consequently, double-membraned bacteria have evolved a fascinating array of protein machines to overcome the challenge of transporting molecules beyond the IM. Moreover, energy from ATP and the proton motive force are associated with the cytoplasm and inner membrane (IM), leaving the periplasm and OM without direct access to these conventional energy sources. Although this complex envelope architecture has many advantages, it also presents many challenges for OM assembly and transport, including the need to move cargo across two lipid bilayers.
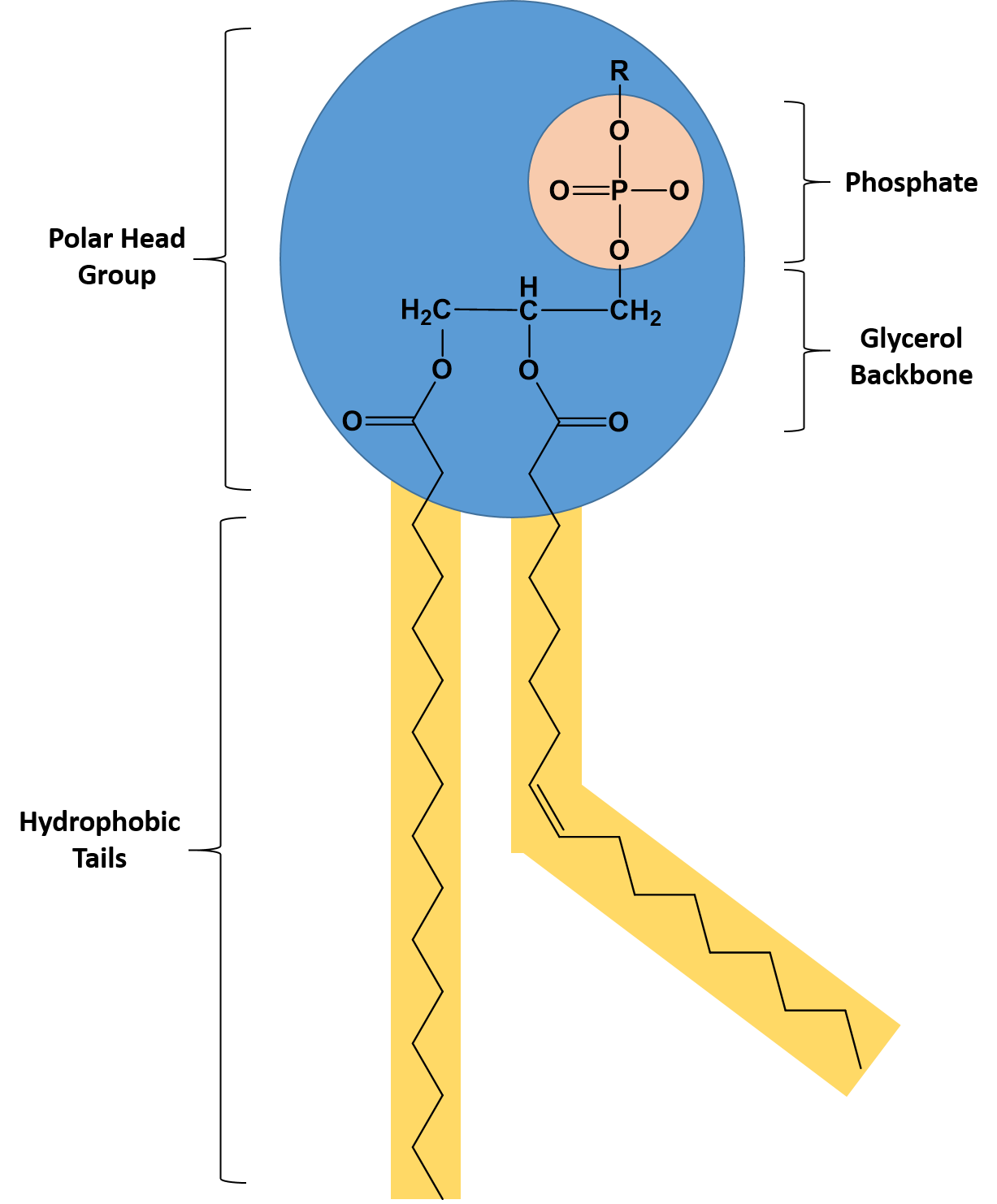
The OM is separated from the inner membrane (IM) by the periplasmic space, which contains the peptidoglycan cell wall. The OM is an asymmetric bilayer, with an outer leaflet of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and a phospholipid inner leaflet. The bacterial outer membrane (OM) is a critical barrier that protects the cell from antibiotics and other environmental threats, and protects pathogenic bacteria from the anti-microbial responses of the host. Our structure provides mechanistic insight into substrate recognition and transport by MlaFEDB. Unexpectedly, two phospholipids are bound to MlaFEDB, suggesting that multiple lipid substrates may be transported each cycle. A continuous transport pathway extends from the MlaE substrate-binding site, through the channel of MlaD, and into the periplasm.
Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of MlaFEDB at 3.05 Å resolution, revealing distant relationships to the LPS and MacAB transporters, as well as the eukaryotic ABCA/ABCG families. The transmembrane subunit, MlaE, has minimal sequence similarity to other transporters, and the structure of the entire inner-membrane MlaFEDB complex remains unknown. An MCE transport system called Mla has been implicated in phospholipid trafficking and outer membrane integrity, and includes an ABC transporter, MlaFEDB. In double-membraned bacteria, phospholipid transport across the cell envelope is critical to maintain the outer membrane barrier, which plays a key role in virulence and antibiotic resistance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
